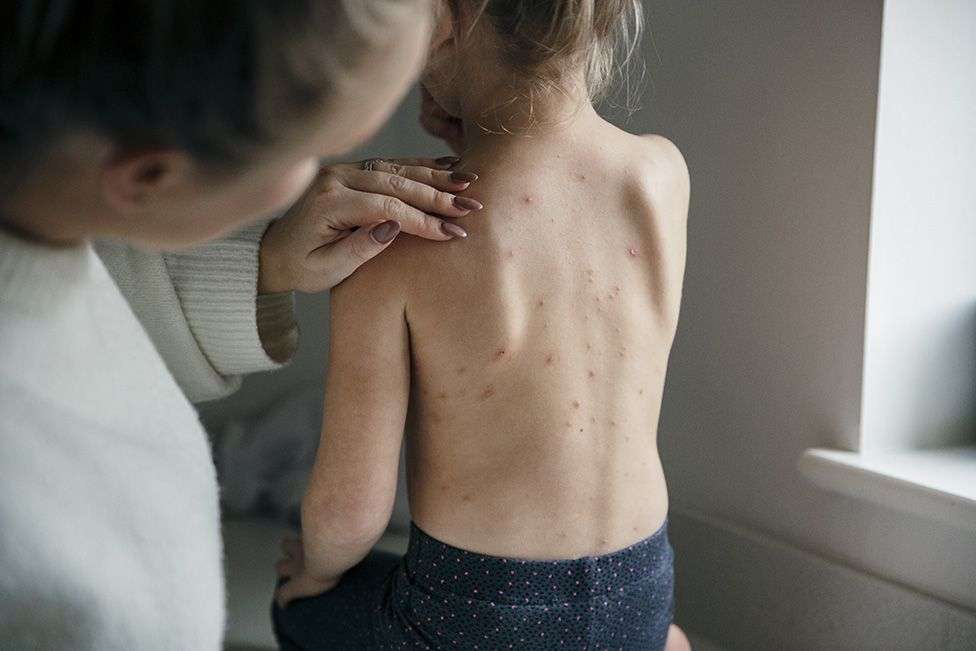
All children in the UK should be given a chickenpox vaccine at 12 and 18 months of age, the NHS is advised.
It will now be up to the government to decide whether to add it to the routine protective jabs that children are offered.
Until now, most parents had to go privately and pay up to £200 to protect their child against the virus, which causes red itchy spots.
Some would even host chickenpox parties to let their child catch it early.
The Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation has also recommended a temporary catch-up programme for slightly older children who've missed out on this initial rollout.
Chickenpox cases decreased during the Covid pandemic due to restrictions on socialising, meaning there is currently a larger pool of children than usual who are unprotected against the highly contagious virus.
Chickenpox can be more severe if you catch it for the first time as a teen or an adult rather than as a young child.
Dr Gayatri Amirthalingam from the UK Health Security Agency said: "Introducing a vaccine against chickenpox would prevent most children getting what can be quite a nasty illness - and for those who would experience more severe symptoms, it could be a life saver.
"The JCVI's recommendations will help make chickenpox a problem of the past and bring the UK into line with a number of other countries that have well-established programmes."
Can you get chickenpox twice?
It is possible but very unusual to get chickenpox more than once.
The vaccine doesn't guarantee lifetime immunity, but it does greatly reduce the risk of someone developing chickenpox or having a bad case.
The shots contain a very small amount of the live virus which has been weakened to teach the body how to fight off an infection without causing full-blown disease.
It's safe for most people, but is not recommended for people who have a weak immune system who could get sick.
Although unpleasant, chickenpox is usually a mild infection, mostly affecting children, that gets better by itself after a week or two.
It's highly infectious - you can catch it by being in the same room as someone with it who is coughing and sneezing.
The characteristic red, itchy spots start appearing one to three weeks after. Some children might have only a few, but others can be covered in them.
Within a few days the spots turn into fluid filled blisters, which are contagious until they crust over to form scabs that eventually drop off and clear up.
There may be flu-like symptoms, such as a high temperature and headache, too.
How to treat mild chickenpox
- Take paracetamol and stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids
- Use cooling creams - such as Calamine lotion - and gels
- Cut your child's fingernails and put socks or gloves on their hands at night to stop them scratching
For some, chickenpox can be really serious and dangerous. In rare cases it can cause a swelling of the brain or other complications.
Keyan Harvey developed necrotising fasciitis, a flesh-eating bug off the back of having chicken pox when he was six.
Hi mum Shavonne Harvey, who is 35 and from Slough, said: "I'm a nurse and I didn't realise just how bad chickenpox can be. I thought he would sail through it but obviously that wasn't the case and after doing some research I realised that some children can be really poorly and even die from it, which was scary."
"It was when he was in surgery that it hit me - I could lose my child to this, to something that everyone thinks is just a little virus."
What about shingles?
Concerns the vaccine programme could inadvertently increase shingles risk for older people are mislaid, says experts.
Shingles, a painful skin rash condition, is caused by the same virus as chickenpox - varicella zoster virus (VZV).
If you have already had chickenpox in the past, being exposed to more as an adult boosts your immunity to shingles.
Vaccinating children against chickenpox removes much of this natural boosting, but experience from other countries suggests it doesn't lead to more shingles cases. The US, Canada and many European nations have been doing it for years.
VZV stays in the body for life and can reactivate, causing shingles, if your immune defences are low.
This can happen because of stress, certain conditions, or treatments like chemotherapy, for example.
People cannot catch shingles from someone with chickenpox. But they can catch chickenpox from someone with shingles if they have not had chickenpox before.